Atoms are composed of subatomic particles: particles that are smaller than the atom.
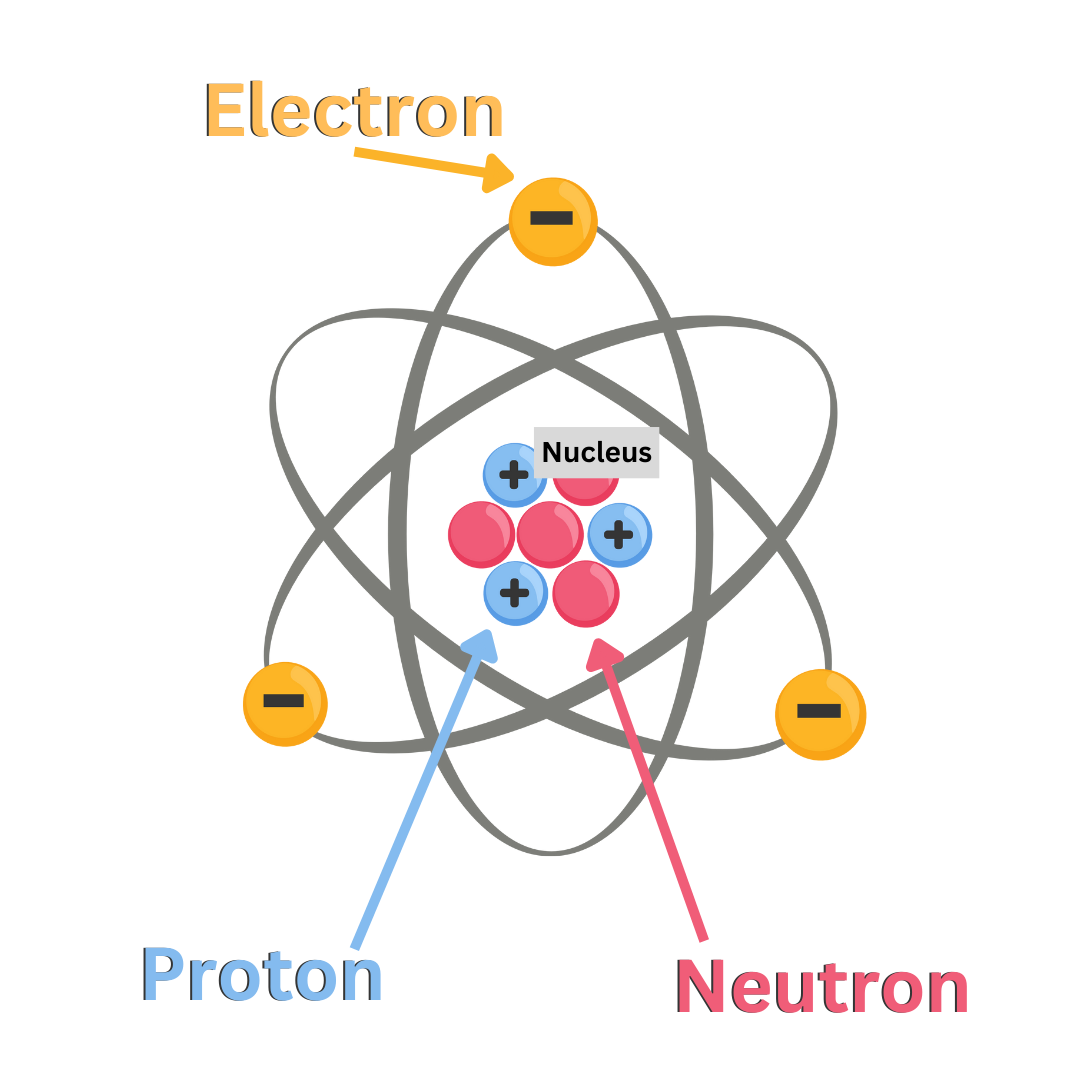
Protons: Subatomic particles with a positive charge.
Electrons: Subatomic particles with a negative charge.
Neutrons: Subatomic particles with a neutral charge. They have no charge.
The protons and neutrons are packed together in the small, dense, center of the atom called the nucleus. The protons try to repulse each other because they are all positive, but the neutral neutrons hold them together, which is why neutrons are called the “glue of the nucleus”.
Electrons orbit around the nucleus just like planets orbit the Sun. Our solar system is mostly empty space. Similarly, the atom is mostly empty space.
Valence Electrons: The outermost electrons of an atom (furthest from the nucleus).
Ions
Atoms have the same amount of protons and electrons, so they have the same number of positive and negative charges, making them neutral overall.
However, electrons can be added/removed from an atom, causing the atom to become charged. Charged atoms are called ions.
Cations: Positively charged ions. Electrons are removed from an atom, causing it to have more protons than electrons.
Anions: Negatively charged ions. Electrons are gained by an atom, causing it to have more electrons than protons.
Molecules
Molecules consist of multiple atoms chemically bonded together. For example, O₂ is a molecule, with two oxygen atoms. CO₂ is a molecule with one carbon atom, and two oxygen atoms.
